
Welcome back 🙂
Hope you all have been enjoying my blog posts so far.
Today’s blog post will cover all the in’s and out’s you want to know about Apple
Is Apple a company of Superior Innovation?
Apple Inc is based in Cupertino, California and was established in 1976 by Steve Jobs Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne. The company was originally called ‘Apple Computer’ for the first 30 years but later dropped the word ‘computer’ in 2007 to reflect the company’s ongoing expansion. On September 30, 2013, Apple surpassed Coca-Cola to become the world’s most valuable brand in the Omnicom Group’s “Best Global Brands” report (Nielson, S 2014).
The company designs, manufactures, and markets mobile communication and media devices, personal computers, and portable digital music players. Apple also sells a variety of related software, services, peripherals, networking solutions, and third-party digital content and applications (Nielson, S 2014).

Steve Jobs quoted, “Apple was a company that was based on innovation. When I left Apple ten years ago, we were ten years ahead of everybody else”. Apple’s business strategy leverages its unique ability to design and develop its own operating systems, hardware, application software, and services to provide new products and solutions to customers with superior ease-of-use, seamless integration, and innovative design (Nielson, S 2014).
Apple is known for its superior innovation and has established a unique reputation in the electronics industry with a loyal customer base. Apple believes that a high-quality buying experience greatly enhances its ability to attract and retain customers. Furthermore, Apple’s strategy also involves enhancing and expanding its own retail and online stores—allowing them to effectively reach more customers (Nielson, S 2014).
The company’s best-known products include Mac computers, the iPod, the iPhone, and the iPad. In 2014, the company sold 26 million iPads during the quarter, compared to 22.9 million in the previous quarter. According to Apple’s recent earnings call, the iPad had a 78% share of the U.S. commercial tablet market.
The graph below highlights how the iPhone dominated majority of Apple’s sales.
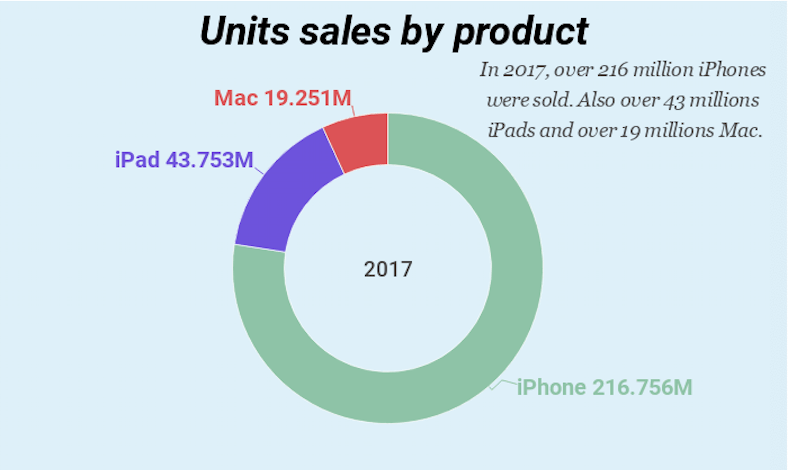
Apple sells and delivers digital content and applications through the iTunes Store, App Store, iBooks Store, and Mac App Store. Apple also sells its products worldwide through third-party cellular network carriers, wholesalers, retailers, and value-added resellers (Nielson, S 2014).
Apple’s strategy:
Apple’s CEO Tim Cook quoted “We never had an objective to sell a low-cost phone. Our primary objective is to sell a great phone and provide a great experience, and we figured out a way to do it at a lower cost.”
Steve Jobs strategy for Apple had four pillars:
- Offer a small number of products.
- Focus on the high end
- Give priority to profits over market share
- Create a halo effect that makes people starve for new Apple products
Apple attempts to increase market demand through differentiation. Additionally, the company’s products have always been designed to be ahead of the curve. Despite high competition, Apple has succeeded in creating demand for its products, giving the company power over prices through product differentiation, innovative advertising, ensured brand loyalty, and hype around the launch of new products. By focusing on customers willing to pay more and maintaining a premium price at the cost of unit volume, Apple also set up an artificial entry barrier to competitors (Nielson, S 2014).
In summary, Apple has become the first American company to reach US$1 trillion in market capitalisation. Apple is the most profitable smart phone manufacturer globally through its sustained competitive advantage, innovation, superior design, marketing and its domination of the advanced consumer electronics supply chain.
Apple’s Business and Revenue Models
The quintessential element of Apple’s business model is its ability to ‘own the consumer’. In short, Apple’s business model is designed to drive consumers into its ecosystem and then hold them there, which has been hugely successful to date and has allowed Apple to wield enormous power in the end-to-end supply chain (Montgomerie & Roscoe 2013).
This business model gives Apple the unique ability to maintain a low cost sourcing strategy while maintaining high price points and subsequently locking the consumer in through high switching penalties.

Apple’s business model affects not only its direct shareholders but also moves markets, which impacts overall macroeconomic performance. In April 2012, Apple’s shares reached a high of $636.00 and market capitalisation surged to $570 billion, more than the value of Google, Microsoft, HP, Dell and Yahoo combined (Montgomerie & Roscoe 2013).
A key facet of Apple’s business model is ensuring that Apple content can only be played on Apple devices, as this helps maintain digital download market share and in turn drives sales volume for profitable hardware devices. The power Apple derives from owning the consumer is evident downstream in the supply chain, for example with retailers, as Apple designs its own in-store displays and places their own sales staff in big retail stores to promote Apple products (Montgomerie & Roscoe 2013).
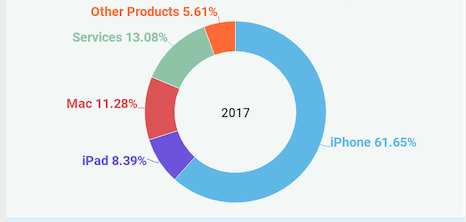
In 2017, over 60% of Apples revenue came from the iPhone. The remaining was the iPad and Mac. Services like digital content, apple pay and apple care make up over 13% of its revenue. Additionally other products such as Apple Tv, Apple Watch, Beats products, iPod touches and other apple branded and third-party accessories make up 5.61% as shown in the diagram below.
Thanks for reading today’s post, hope you enjoyed 🙂
References
Clarke, T & Boersma, M 2017, Apple’s $1 trillion riches, UTS, Sydney, viewed 4 September 2019, http://www.martijnboersma.com/apple-innovation-exploitation
Cuofano, G 2018, Apple Business Model, FourWeekMBA, n.p, viewed 4 September 2019, https://fourweekmba.com/apple-business-model/
Cuofano, G 2018, Apple Business Strategy, FourWeekMBA, n.p, viewed 4 September 2019, https://fourweekmba.com/apple-business-strategy/
Montgomerie, J & Roscoe, S 2013, ‘Owning the consumer—Getting to the core of the Apple business model’, vol. 37, no. 4, pp. 290-299, viewed 4 September 2019, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S015599821300032X#targetText=The%20source%20of%20Apple’s%20recent,and%20tablets)%20to%20drive%20growth.
Nielson, S 2014, A Leading Supply Chain, Market Realist, n.p, viewed 4 September 2019, https://articles2.marketrealist.com/2014/02/apple-supply-chain/
Nielson, S 2014, Apple’s Premium Pricing Strategy and Product Differentiation, Market Realist, n.p, viewed 4 September 2019, https://articles2.marketrealist.com/2014/02/apples-premium-pricing-strategy-product-differentiation/
Great info very informative !
LikeLike